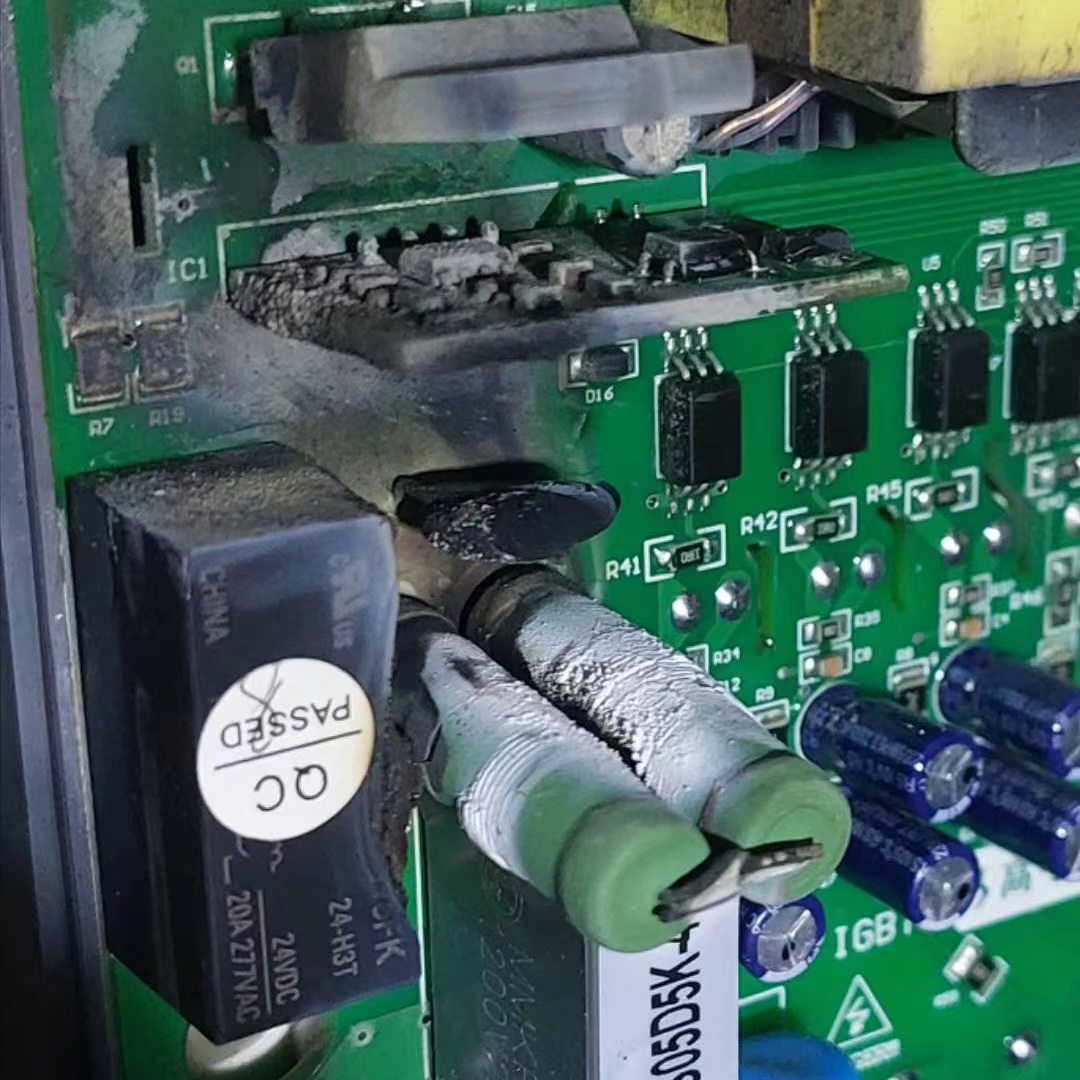
Common Causes of Inverter Failures
I am not a design engineer, but as a
quality management professional, I would like to outline some major causes of
inverter failures that I’ve encountered:
1. Lack of Phase Loss or Overvoltage
Protection: If the circuit design of a three-phase inverter does not take into
account input phase loss protection or overvoltage protection, the inverter can
easily get damaged during operation.
2. Improper Circuit Design: Poor circuit
design is another key reason why inverters are prone to failure.
3. Component Selection in the Early
Development Stage: The selection of all electronic components during the design
and development stage is crucial. The technical confirmation of all components
before production is especially important.
4. Temperature Control in Soldering
Processes: Temperature control during reflow soldering, wave soldering, and
manual soldering of components is critical. Components that suffer heat damage
may not show faults during factory testing but could have a shortened lifespan
or fail under high current and voltage conditions once they are in the market.
In summary, aside from failures caused by
static electricity, factors such as circuit design integrity, component
selection, and temperature control during soldering are major contributors to
inverter failures under high current and voltage conditions.